Every year new personal finance apps appear, promising to make money management effortless. They come with colorful dashboards, automated syncing, and sometimes even AI-driven insights. At first glance they look like the future of financial planning. Yet despite all this innovation, spreadsheets continue to hold their ground as one of the most trusted tools in personal finance.
Spreadsheets may not be flashy, but they are powerful. They provide something apps rarely can: complete transparency, infinite flexibility, and a structure that adapts to your life rather than forcing you into rigid categories. While apps can track what has already happened, spreadsheets can show you what might happen in the future. This ability to look forward makes them invaluable for anyone who wants to take control of their financial life.
Finance Apps, Spreadsheets, and Advisors: A True Comparison
When thinking about financial planning, you generally have three main options: using an app, creating a spreadsheet, or hiring a professional advisor. Each path offers benefits, but each also carries drawbacks.
Finance apps excel at convenience. They automatically import transactions, categorize them, and create attractive summaries. They are useful if your main goal is simply to understand past spending habits. However, their limitations quickly become clear. They rarely allow deep customization, and they often fail to capture the complexity of real-life financial situations.
Advisors provide human expertise and accountability. They can create personalized strategies and keep you disciplined. But professional advice comes with significant costs, and sometimes with conflicts of interest. For many households, paying thousands each year in fees is not realistic.
Spreadsheets fall in between. They are transparent, customizable, and long-lasting. They may require a bit of setup, but once built, they give you unmatched control over your financial future. They allow you to both track and project, creating a planning tool that grows with you instead of restricting you.
| Tool | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Finance Apps | Automated transaction syncing, attractive dashboards, beginner-friendly | Limited projections, rigid categories, monthly fees, data privacy concerns |
| Spreadsheets (Excel/Google Sheets) | Transparent, fully customizable, free or low cost, long-term projections | Requires setup or a template, less automated |
| Advisors | Human guidance, tailored strategies, accountability | Expensive, ongoing fees, may push products |
Why Spreadsheets Still Outperform Apps
The first reason is transparency. With a spreadsheet you can see every formula. If you want to know exactly how your projected retirement balance is calculated, you can open the cell and check the math. Nothing is hidden behind polished graphics.
The second reason is flexibility. Spreadsheets adapt to any situation, no matter how unique. If you have multiple income sources, investments across several asset classes, or irregular freelance work, you can model all of it. You are not forced into someone else’s definition of what “normal” finances should look like.
The third reason is permanence. Spreadsheets do not depend on a subscription or a company’s survival. They are yours to keep, whether stored on your device or in the cloud. Apps can shut down, increase fees, or restrict features. A spreadsheet continues working as long as you open it.
Finally, and most importantly, spreadsheets allow projection. Most apps focus on recording past spending. Spreadsheets, by contrast, help you look forward. You can see how your net worth changes under different return assumptions, or how retiring early would alter your cash flow. This ability to model future outcomes makes spreadsheets far more than record-keeping tools. They become decision-making systems.
How to Build a Financial Planning Spreadsheet
The process of creating a spreadsheet for financial planning begins with establishing a clear picture of where you stand today, then building the framework to see where you might be headed.
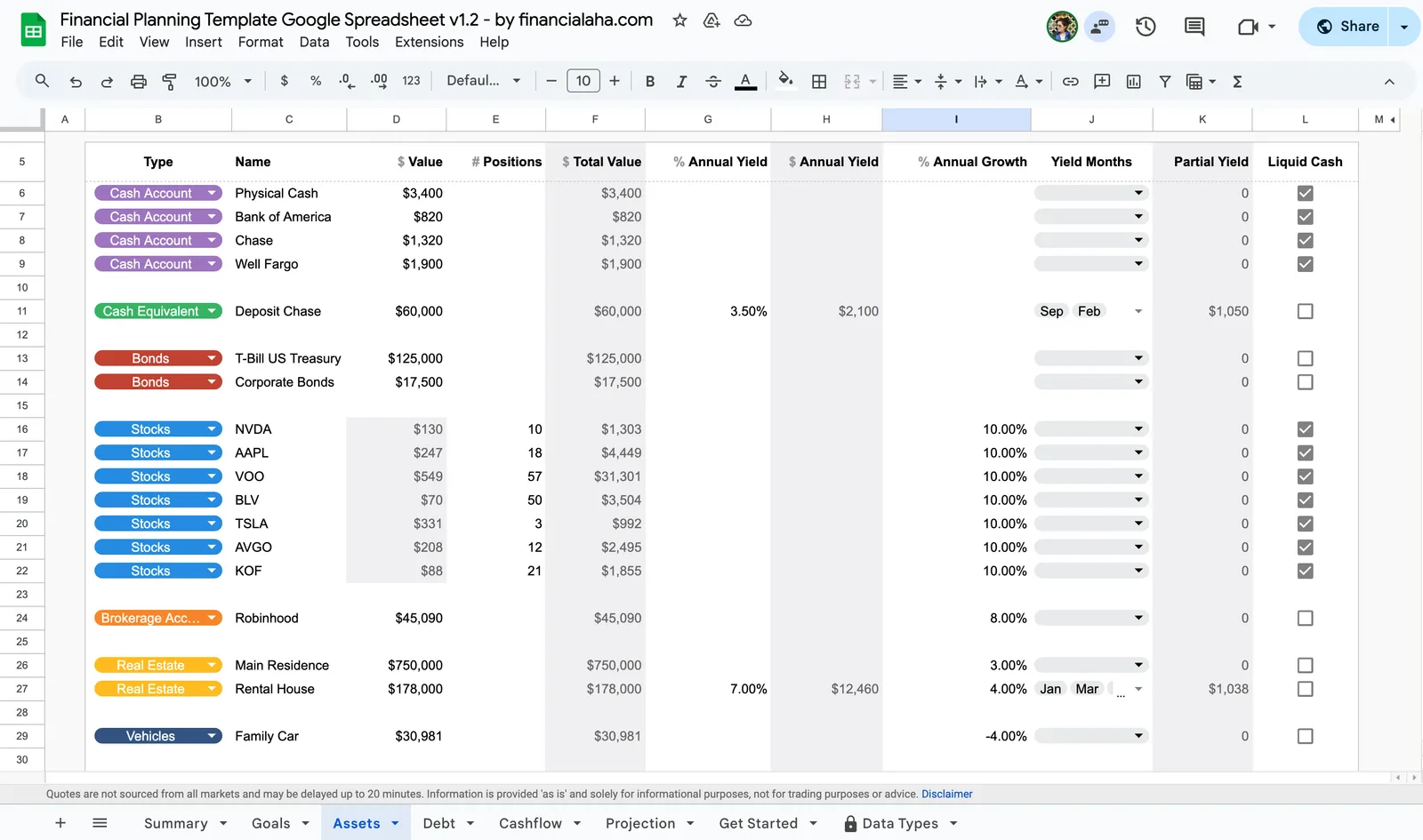
Start by creating a balance sheet that lists every asset you own and every debt you owe. Assets include cash, investment accounts, retirement savings, and real estate. Debts include credit cards, student loans, mortgages, and car loans. This gives you a snapshot of your current net worth - the foundation everything else builds on.
From there, track your monthly cash flow by creating categories for income and expenses. Income might include salary, dividends, or side business revenue. Expenses typically cover both essentials and discretionary items. Tracking this data over time reveals patterns and shows how much you can consistently save or invest. Many people discover surprising insights just from this step alone - categories that seemed small individually can add up significantly over a year.
The next layer adds growth assumptions, and this is where spreadsheets truly demonstrate their value. You can input assumptions for investment returns, debt interest rates, or inflation. A simple formula such as future value will project how regular contributions grow over time. By adjusting assumptions you can instantly see different outcomes - what happens if returns are 6% instead of 8%, or if you increase contributions by $200 per month.
With cash flow data and growth assumptions in place, you can project your balance sheet into the future. Build scenarios such as “retire at sixty-five” versus “retire at fifty-five,” or compare paying off debt faster against investing more aggressively. This forward-looking capability is what separates spreadsheets from simple tracking tools.
Finally, consider adding charts to visualize the results. Charts can show how your net worth evolves, when your debts are eliminated, or how much retirement savings you will accumulate. Visuals make complex information easier to grasp and more motivating to follow. A well-designed chart showing steady progress toward a goal can be surprisingly powerful for maintaining long-term focus.
Scenarios Where Spreadsheets Shine
Imagine a freelancer whose income changes every month. A budgeting app that expects steady paychecks will always misinterpret their finances. A spreadsheet, on the other hand, can include best case, average case, and worst case income projections. This helps the freelancer plan for lean months without losing sight of long-term goals.
Now consider someone in the FIRE community, aiming to retire early. They need to know how a three percent withdrawal rate compares to a four percent withdrawal rate across forty years. Most apps cannot provide this level of precision. A spreadsheet can. It allows them to model market returns, inflation, and spending in detail, helping them choose a safe path to financial independence.
Finally, think about a family saving for multiple goals at once. They may want to fund college tuition, pay off a mortgage, and build retirement savings. Apps rarely handle overlapping goals effectively. In a spreadsheet, the family can model all three, adjusting contributions and seeing how one goal affects another. This gives them a clear picture of trade-offs and priorities.
In each of these cases, spreadsheets do not just record numbers. They enable planning that is personalized and actionable.
Why Templates Make It Easier to Start
While creating a spreadsheet from scratch is powerful, it can also feel intimidating. Building formulas for investment growth, inflation, and cash flow takes time and some technical skill. For many people this effort becomes a barrier to getting started.
Templates solve this problem. They offer a structured foundation with ready-made formulas and dashboards. At the same time, they preserve the flexibility to adjust and expand. You get the best of both worlds: a professional model without the need to design it yourself.
The FinancialAha Financial Planning Spreadsheet was designed for exactly this purpose. It is built in both Google Sheets and Excel, making it accessible on any device. It includes sections for assets, debts, income, and expenses, along with built-in projections for net worth and retirement. Dashboards visualize your progress and allow you to test scenarios instantly. With a template like this you can move past setup and focus on what really matters: making better financial decisions.
Common Questions
What is a financial planning spreadsheet?
A financial planning spreadsheet is a structured file in Google Sheets or Excel that helps you track your current finances and project your future. It typically includes sections for income, expenses, assets, debts, and investment assumptions. The goal is to show not only where you stand today but where you could be years from now. Unlike apps that focus primarily on past transactions, a well-built spreadsheet becomes a tool for modeling different scenarios and making informed decisions about your financial direction.
Which is better for financial planning, Google Sheets or Excel?
Google Sheets is often preferred for easy sharing and cloud access across devices - you can check your finances from your phone, laptop, or any computer with an internet connection. Excel tends to be stronger for advanced formulas or very large datasets, and some people simply prefer working with desktop software. Both work well for financial planning, and the choice depends on whether convenience or advanced power matters more to you. Many of the templates available today work in both environments.
Can spreadsheets replace finance apps?
For many people, yes. While apps are convenient for automatically importing transactions, spreadsheets provide much greater flexibility and projection capabilities. Apps excel at telling you what happened last month. Spreadsheets can do that too, but they also let you explore what might happen next year, in five years, or at retirement. For long-term planning, spreadsheets are often the more powerful choice.
How can a spreadsheet help with retirement planning?
Retirement planning involves many variables - current savings, planned annual contributions, expected investment returns, retirement expenses, and how long retirement might last. A spreadsheet can hold all of these inputs and show you how they interact. Using functions such as future value, you can project how your investments will grow and how long they might last under different scenarios. Want to see what happens if you retire two years earlier? Change one number and the entire projection updates.
Why not just use an app like Mint, YNAB, or ProjectionLab?
Apps are good at looking backward. They can show how much you spent last month, but they are often less effective at showing how today’s decisions shape your future. A spreadsheet can do both - track what has happened and project what might happen. It gives you transparency and control that apps rarely match. Some people use apps for day-to-day tracking and spreadsheets for longer-term planning, combining the convenience of automation with the depth of custom modeling.
The Future Is Still Spreadsheet-Shaped
Financial planning does not have to be outsourced to a paid app or an advisor. The truth is that some of the best financial plans are still built in spreadsheets. They are transparent, flexible, and permanent. Most importantly, they give you the power to look forward and test different futures, not just analyze the past.
By adopting a spreadsheet-based system, you can move beyond the question of “Where did my money go?” and begin asking the more powerful question: “Where is my money taking me?” That shift in perspective is what makes spreadsheets one of the most enduring and effective tools in financial planning today.
Ready to build your own plan? Download the Financial Planning Spreadsheet here and start turning your numbers into a clear roadmap for the future.
Related Templates
- Financial Planning Template - The comprehensive spreadsheet for tracking net worth, cash flow, and projecting your financial future
- Net Worth Tracker - A focused tool for tracking assets and liabilities
- Annual Budget Planner - Full year budgeting with all 12 months in one view
- Monthly Budget Template - Monthly expense tracking with budget targets